-
 +10 +4
+10 +4The dawn of speech was millions of years earlier than previously thought
For more than fifty years, scientists have thought that the origin of speech depended on one pivotal moment 200,000 years ago. That’s when the human larynx descended, elongating the vocal tract. Until now, this physiological innovation was seen as the root of humans’ unique ability to communicate verbally with one another. But a new paper suggests that estimate may be off — by a couple of million years.
-
 +7 +1
+7 +1Early humans domesticated themselves, new genetic evidence suggests
When humans started to tame dogs, cats, sheep, and cattle, they may have continued a tradition that started with a completely different animal: us. A new study—citing genetic evidence from a disorder that in some ways mirrors elements of domestication—suggests modern humans domesticated themselves after they split from their extinct relatives, Neanderthals and Denisovans, approximately 600,000 years ago.
-
 +24 +2
+24 +2The Last of The Neanderthals Carved This Eagle Talon Into a Powerful Symbol
We invoke their name as an insult, but continuing discoveries about the extinct Neanderthal culture suggest the existence of a rich, complex symbolism we still do not fully understand. Now, we have another artefact to admire.
-
 +14 +3
+14 +3Long strand of DNA from Neanderthals found in people from Melanesia
Many people have DNA inside them that they inherited from extinct hominins like the Neanderthals – and now we know that in some cases it isn’t just tiny snippets but long stretches. Over the past decade, genetic analysis of human DNA has revealed that ancient humans must have interbred many times with other hominins such as Neanderthals. The result is that DNA from these extinct groups can be found in many human populations today.
-
 +14 +4
+14 +4New evolution-busting drug overcomes resistance in aggressive breast cancers - The Institute of Cancer Research, London
A new type of drug that blocks one of cancer’s key evolutionary escape routes from chemotherapy could be used to treat aggressive breast cancers, a new study has shown.
-
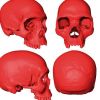 +14 +2
+14 +2Scientists Find the Skull of Humanity’s Ancestor, on a Computer
By comparing fossils and CT scans, researchers say they have reconstructed the skull of the last common forebear of modern humans.
-
 +19 +3
+19 +3The Genetic Program That Governs the Birth of Vision
How is the retina formed? And how do neurons differentiate to become individual components of the visual system? By focusing on the early stages of this complex process, researchers at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland, in collaboration with the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), have identified the genetic programmes governing the birth of different types of retinal cells and their capacity to wire to the correct part of the brain, where they transmit visual information.
-
 +16 +1
+16 +1Humans, chimpanzees and bonobos share eye patterns
Scientist have detected the same eye patterns in humans, chimpanzees and bonobos despite contradictions from previous studies. Scientists have shown that the contrast between the white of human eyes, the sclerae, and the iris allows others to tell the direction of our gaze. Such ability allows humans to commence social learning and other social skills.
-
 +4 +1
+4 +1The Paleozoic diet: Why animals eat what they eat
In what is likely the first study to look at how dietary preferences evolved across the animal kingdom, UA researchers looked at more than a million species, going back 800 million years. The team reports several unexpected discoveries, including that the first animal likely was a carnivore and that humans, along with other omnivores, belong to a rare breed.
-
 +13 +2
+13 +2Poll: Two in Five Americans Still Believe God Created Humans 10,000 Years Ago
A new Gallup poll shows that 40 percent of American adults comply to a strict view of creationism, in which God brought humans into existence within the last 10,000 years. More encouragingly, a record number of Americans now say God had absolutely nothing to do with it.
-
 +15 +2
+15 +2Enigmatic skull suggests our human species reached Europe 210,000 years ago
The claim is generating excitement as well as skepticism among experts who study human evolution.
-
 +10 +1
+10 +1Dogs' eyes evolve to appeal to humans
If a dog has eyes that seem to be telling you something or demanding your attention, it could be evolution's way of manipulating your feelings. Researchers have found that dogs have evolved muscles around their eyes, which allow them to make expressions that particularly appeal to humans.
-
 +25 +8
+25 +8Ecuador gives US military permission to use Galapagos island as airfield
Criticising agreement, former president says Pacific archipelago is 'not for gringo use.' By Tom Embury-Dennis.
-
 +4 +1
+4 +1Unraveling the Mystery of Human Bipedality
Paleoanthropologist Carol Ward explains how walking upright marked a milestone in hominin history.
-
 +22 +4
+22 +4New Research Has Identified the Genes That Might Hold the Key of Human Evolution
Scientists have found that dozens of genes similar across different organism are unique to humans, and this could hold the key to the evolution of species. Researchers from the University of Toronto, Canada, have found out that these genes codes are transcription factors (TFs) and are controlling the gene activity. The study was published in the Nature Genetics Journal.
-
 +8 +4
+8 +4Scientists Think They've Found an 'Ingredient' That Drove The Cambrian Explosion
As the content of Earth's atmosphere changes over time, the course of animal evolution itself might change.
-
 +21 +6
+21 +6In the deep, dark ocean fish have evolved superpowered vision
When the ancestors of cave fish and certain crickets moved into pitchblack caverns, their eyes virtually disappeared over generations. But fish that ply the sea at depths greater than sunlight can penetrate have developed super-vision, highly attuned to the faint glow and twinkle given off by other creatures. They owe this power, evolutionary biologists have learned, to an extraordinary increase in the number of genes for rod opsins, retinal proteins that detect dim light.
-
 +10 +1
+10 +1Scientists Gave Wolves Touchscreens to See If They're Friendlier Than Dogs
Who gives out more treats, dogs or wolves? By Becky Ferreira.
-
 +20 +3
+20 +3Scientists discover evolutionary link to modern-day echinoderms
Scientists at The Ohio State University have discovered a new species that lived more than 500 million years ago—a form of ancient echinoderm that was ancestral to modern-day groups such as sea cucumbers, sea urchins, sea stars, brittle stars and crinoids. The fossil shows a crucial evolutionary step by echinoderms that parallels the most important ecological change to have taken place in marine sediments.
-
 +31 +5
+31 +5Life May Have Evolved Before Earth Finished Forming
The first organisms may have evolved before the rocky planets formed. By Mike Wall.
Submit a link
Start a discussion




















