-
 +18 +1
+18 +1Rabies breakthrough offers fresh hope in battle against deadly virus
Researchers have discovered a way to stop rabies from shutting down critical responses in the immune system, a breakthrough that could pave the way for new tools to fight the deadly disease. Rabies kills almost 60,000 people each year, mostly affecting poor and rural communities.
-
 +14 +1
+14 +1China approves seaweed-based Alzheimer's drug. It's the first new one in 17 years
Authorities in China have approved a drug for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, the first new medicine with the potential to treat the cognitive disorder in 17 years. The seaweed-based drug, called Oligomannate, can be used for the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer's, according to a statement from China's drug safety agency. The approval is conditional however, meaning that while it can go on sale during additional clinical trials, it will be strictly monitored and could be withdrawn should any safety issues arise.
-
 +6 +1
+6 +1Study finds acid reducers may pose risk for children
The use of acid reducers among children is on the rise and so are potential side effects, which is sparking concern according to a recent study.
-
 +16 +1
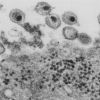
+16 +1Scientists detect a first new strain of HIV virus in 19 years
For the first time in 19 years, a team of scientists have detected a new strain of HIV. The strain is a part of the Group M version of HIV-1, the same family of virus subtypes to blame for the global HIV pandemic, according to Abbott Laboratories, which conducted the research along with the University of Missouri, Kansas City.
-
 +14 +1
+14 +1Woman told she had IBS by four different GPs actually had cancer
Despite finding blood when she went to the toilet, Deborah Cameron was told she had nothing 'major' to worry about.
-
 +3 +1
+3 +1Pediatricians endorse weight loss surgery for severely obese kids and teens
The American Academy of Pediatrics now recommends that metabolic and bariatric surgery should be considered as a safe treatment option for children and teens with severe obesity -- something that is normally not covered by insurance for young people.
-
 +3 +1
+3 +1Resistance to Antibiotics Doubles in Twenty Years
New research findings from 18 European countries show that the bacterial resistance to antibiotics is increasing and this is causing serious medical issues.
-
 +17 +1
+17 +1The world's first artificial womb for humans
Scientists in the Netherlands say they are within 10 years of developing an artificial womb that could save the lives of premature babies. Premature birth, before 37 weeks, is globally the biggest cause of death among newborns.
-
 +18 +1
+18 +1Flu vaccine offered to every primary school child in England
Every primary school child in England is to be offered vaccination against winter flu in an attempt to safeguard them and their family from the virus, the health service has announced, promising no shortage of vaccines regardless of the Brexit outcome. This year’s flu vaccination campaign will be the biggest ever, with 25 million people offered vaccines free, including 600,000 school children aged 10-11. Children are considered “super-spreaders”, liable to infect others in their family and a danger to the elderly. All children aged two to 11 will be offered the nasal spray vaccine in the coming weeks.
-
 +14 +1
+14 +1New evolution-busting drug overcomes resistance in aggressive breast cancers - The Institute of Cancer Research, London
A new type of drug that blocks one of cancer’s key evolutionary escape routes from chemotherapy could be used to treat aggressive breast cancers, a new study has shown.
-
 +20 +1
+20 +1N.Y. Declares the End Is Near for AIDS Epidemic
There was a time when the diagnosis of H.I.V. was a death sentence, when thousands of New Yorkers, primarily gay men, succumbed to AIDS-related illnesses, and the end of the epidemic seemed both medically and mentally impossible.
-
 +4 +1
+4 +1Can MDMA Help Patients with PTSD?
Recent media reports describe medical professionals treating patients with MDMA (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine) to combat post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). This may seem like an unorthodox approach or the musings of a few fringe figures. While unorthodox, neither is the case. The treatment has been rigorously tested, and the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has allowed the treatment to progress to Phase 3 clinical trials. It has also received Breakthrough Therapy status.
-
 +16 +1
+16 +1Skin cancer: Half of people surviving advanced melanoma
More than half of patients can now survive a deadly skin cancer that was considered untreatable just a decade ago, say UK doctors. Ten years ago only one-in-20 patients would live for five years after being diagnosed with late-stage melanoma. Most would die in months. But drugs to harness the body's immune system mean 52% now live for at least five years, a clinical trial shows.
-
 +16 +1
+16 +1AI equal with human experts in medical diagnosis, study finds
Artificial intelligence is on a par with human experts when it comes to making medical diagnoses based on images, a review has found. The potential for artificial intelligence in healthcare has caused excitement, with advocates saying it will ease the strain on resources, free up time for doctor-patient interactions and even aid the development of tailored treatment. Last month the government announced £250m of funding for a new NHS artificial intelligence laboratory.
-
 +17 +1
+17 +1Light-activated metal catalyst destroys cancer cells’ vital energy source
A space-age metal that formed part of the asteroid that destroyed the dinosaurs could provide a new method of treating cancer tumours selectively using light.
-
 +15 +1
+15 +1Taking A Placebo Can Reduce Anxiety Before An Exam — Even When You Know The Pills Are Inert
The placebo effect is a curious phenomenon. A wealth of literature has shown that inert treatments can not only produce medical benefits like pain relief, but also have cognitive effects like boosting creativity and learning. And while many of those studies involve misleading people into thinking that they are receiving an effective intervention, a new study in Scientific Reports shows that this deception is not always necessary. Researchers have found that taking a placebo can reduce people’s anxiety before a test — even when they know they are taking an inactive pill.
-
 +3 +1
+3 +1Type 2 Diabetes Is About More Than Just Insulin
Insulin imbalance may not be the only cause of the onset of diabetes. Researchers at the University of Geneva have highlighted another mechanism: the liver appears to have the ability to produce a significant amount of glucose outside of any hormonal signal.
-
 +7 +1
+7 +1Mind-blowing drug trials show it’s possible to reverse biological age
The relentless march of time will eventually claim all of our lives — or at least that’s the reality we’ve all come to expect. Short of finding the mythical Fountain of Youth, there’s not much any of us can do about getting older, but new drug trials suggest that might eventually change, and the results have shocked even the scientists who were conducting the experiments.
-
 +2 +1
+2 +1Malaria breakthrough as scientists find ‘highly effective’ way to kill parasite
Human trials of new antimalarial drugs are in the pipeline after Kenyan scientists successfully used bacteria to kill the parasite that causes the disease. The Kenya Medical Research Institute (Kemri) and global health partners say the breakthrough could potentially lead to the development of a new class of drugs in less than two years.
-
 +28 +1
+28 +1Say goodbye to temporary fillings: scientists successfully use a gel to regrow tooth enamel
Dental fillings may soon be a thing of the past thanks to this latest breakthrough from Chinese scientists. Enamel is the mineralized substance that protects the surface of teeth. Though it is one of the toughest tissues in our bodies, it is prone to degradation over time particularly as a result of consistent exposure to certain acids that are found in food and drinks.
Submit a link
Start a discussion




















