-
 +16 +5
+16 +5U.S. monkeypox cases may be peaking, experts say
Monkeypox cases in some large U.S. cities appear to be declining, matching trends seen in Europe, and experts are cautiously optimistic the outbreak may have peaked in places hit hardest hit by the virus. The World Health Organization earlier on Thursday said monkeypox cases reported globally declined 21% last week, after a month-long trend of rising infections, but noted that U.S. cases continued to rise.
-
 +13 +4
+13 +4Biologic therapy for atopic disease appears safe during pregnancy, more research needed
The use of biologics to treat atopic disease before and during pregnancy does not seem to negatively affect maternal or fetal outcomes, according to a review published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice.
-
 +16 +5
+16 +5UBC researchers say they've found 'weak spot' in all COVID-19 variants that could lead to better treatment | CBC News
Researchers at the University of British Columbia have discovered what they describe as a "weak spot" in all major variants of the virus that causes COVID-19 — a revelation they believe could open the door for treatments to fight current and future mutations.
-
 +24 +2
+24 +2With advances in medicine, could 80 become the new 40?
For all the advances in medical technology humans have developed, there is one thing it hasn't been able to do: stop us from getting old. We've managed to extend the human lifetime dramatically in the last couple of centuries, greatly diminishing infant and child mortality and pushing back on disease with antibiotics and vaccines.
-
 +21 +3
+21 +3Do not try this at home: Medieval medicine under the spotlight in major new project
How did our medieval ancestors use dove faeces, fox lungs, salted owl or eel grease in medical treatments? A Wellcome funded project at Cambridge University Library is about to find out.
-
 +3 +1
+3 +1The quest to show that biological sex matters in the immune system
Sabra Klein is deeply aware that sex matters. During her PhD research at Johns Hopkins University, Klein learned how sex hormones can influence the brain and behavior. “I naively thought: Everybody knows hormones can affect lots of physiological processes—our metabolism, our heart, our bone density. It must be affecting the immune system,” she says.
-
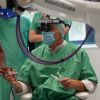 +18 +5
+18 +5First completely robot-supported microsurgical operations performed
A great success for robotic microsurgery not only in Münster but worldwide. A team led by Dr. Maximilian Kückelhaus and Prof. Tobias Hirsch from the Centre for Musculoskeletal Medicine at the University of Münster has carried out the first completely robot-supported microsurgical operations on humans.
-
 +21 +4
+21 +4Cornea made from pig collagen gives people who were blind 20/20 vision
Corneas made from pig collagen have restored sight for people who were previously legally blind or visually impaired. Two years after the operations, none of the recipients have reported serious complications or adverse side effects.
-
 +11 +3
+11 +3Scientists claim to have developed 'cure for blindness'
A protein implant could cure blindness, according to a new study. Researchers found no one who had the operation was still blind two years later and three people who were blind ended up with 20:20 vision.
-
 +18 +1
+18 +1Man wakes up with bat on his neck, later dies after refusing rabies vaccine
A colony of bats was later discovered in the man's Illinois home, and he refused treatment despite the warnings.
-
 +4 +1
+4 +1Using only skin cells, Israeli lab makes synthetic mouse embryos with beating hearts
An Israeli lab has grown synthetic mouse embryos with brains and beating hearts — in an egg-free sperm-free procedure that used stem cells taken from skin. The breakthrough, published on Monday in the peer-reviewed journal Cell, represents the first time that an advanced embryo of any species has been created from stem cells alone, cell biologist Prof. Jacob Hanna of the Weizmann Institute of Science told The Times of Israel.
-
 +4 +1
+4 +1California will start producing insulin and selling it at a cheaper rate soon
California will start producing insulin and selling it at a cheaper rate as Insulin is held prisoner by a health care system in the United States that is persistently resistant to improvements, allowing firms to dominate the market and maximize profits.
-
 +20 +3
+20 +3Eating More Ultra-processed Foods Associated with Increased Risk of Dementia
People who eat the highest amounts of ultra-processed foods like soft drinks, chips and cookies may have a higher risk of developing dementia than those who eat the lowest amounts, according to a new study published in the July 27, 2022, online issue of Neurology®,
-
 +13 +2
+13 +2Fourth patient seemingly cured of HIV
A man who has lived with HIV since the 1980s seems to have been cured in only the fourth such case, say doctors. He was given a bone marrow transplant to treat blood cancer leukaemia from a donor who was naturally resistant to the virus. The 66-year-old, who does not want to be identified, has stopped taking HIV medication.
-
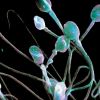 +16 +3
+16 +3What we know so far about how covid-19 affects sperm
Covid-19 infections can lower sperm count and the virus may even bind to receptors on the surface of sperm cells. However, there is no evidence to suggest that the effects differ to those seen after other illnesses that involve fever, such as the flu.
-
 +4 +1
+4 +1Antidepressants work, but just not how scientists thought they worked
Most clinical trials of antidepressants were done decades ago in people with severe depression recruited from specialist mental health services. Yet most people who take these drugs have mild to moderate depression. We wanted to know whether a common antidepressant called sertraline works for this group. We found that, indeed, it does work, but differently from how we expected.
-
 +17 +3
+17 +3The Marburg virus: urgent need to contain this close cousin of Ebola
The chances of surviving Marburg are improved if there’s early supportive care with rehydration and symptomatic treatment.
-
 +25 +2
+25 +2Blood pressure e-tattoo promises continuous, mobile monitoring
Blood pressure is one of the most important indicators of heart health, but it's tough to frequently and reliably measure outside of a clinical setting. For decades, cuff-based devices that constrict around the arm to give a reading have been the gold standard. But now, researchers at The University of Texas at Austin and Texas A&M University have developed an electronic tattoo that can be worn comfortably on the wrist for hours and deliver continuous blood pressure measurements at an accuracy level exceeding nearly all available options on the market today.
-
 +15 +3
+15 +3Major Step Forward In Fabricating An Artificial Heart, Fit For A Human
The future of cardiac medicine involves tissue engineering. It includes the creation of a human heart for transplant. Researchers at Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have created the first biohybrid model of beating cardiac cells aligned helically. This model demonstrated that muscle alignment does, in fact, significantly increase the amount of blood the ventricle can pump with each contraction.
-
 +24 +3
+24 +3Loss of male sex chromosome leads to earlier death for men
According to recent study from the University of Virginia School of Medicine, the loss of the male sex chromosome as men age causes the heart muscle to scar and can result in fatal heart failure. The discovery could provide some insight into why males often pass away at an earlier age than women.
Submit a link
Start a discussion




















