-
 +15 +2
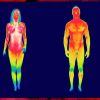
+15 +2Human Body Temperature Is Getting Cooler, Study Finds
Whether you’ve got a wrist sprain a stomachache or a disease that is chronic, one of the things nurses and doctors will do in a consultation will be take your temperature. A temperature that is standard means your body is humming across. A temperature means you demonstrates that your body could be fighting with an illness, and have a fever.
-
 +16 +3
+16 +3Lungs 'magically' heal damage from smoking
The effect has even been seen in people who had smoked for 40 years.
-
 +15 +4
+15 +4Lungs 'magically' heal damage from smoking
The effect has even been seen in people who had smoked for 40 years.
-
 +12 +2
+12 +2You Could Probably Hibernate
Complaining about winter is one of the few remaining bastions of reliably safe small talk. Some people protest—I absolutely love freezing—but most will happily engage in winter bashing. In addition to widespread access to heated homes, offices, and vehicles, new industries continue to emerge on the promise of combatting winter. Moisturizing skin-care regimens are sold as the only way to keep our skin in one piece, and massive down coats are deemed necessary for spending even a few minutes outside. Sun-imitating lamps and vitamins promise to help us maintain a will to live.
-
 +14 +2
+14 +2A new study shows an animal's lifespan is written in the DNA. For humans, it's 38 years
Knowing an animal's normal lifespan is hugely important for conservation efforts, but it's harder to find out than you'd think.
-
 +2 +1
+2 +1Why When You Eat Might Be as Important as What You Eat
About 1 in 3 American adults have metabolic syndrome, a group of early warning signs for increased risk of type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. To help avoid such health problems, these folks are often advised to pay close attention to the amount and type of foods they eat. And now it seems there may be something else to watch: how food intake is spaced over a 24-hour period.
-
 +1 +1
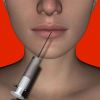
+1 +1The Limits And Benefits Of Botox
As we age, we lose collagen in our skin. Collagen is responsible for helping the skin maintain its elasticity. It's what helps overturn cells to make room for new ones. Once our skin starts producing less collagen, it never regains its ability to do it as before.
-
 +14 +1
+14 +1Good noise, bad noise: white noise improves hearing
Noise is not the same as noise – and even a quiet environment does not have the same effect as white noise. With a background of continuous white noise, hearing pure sounds becomes even more precise, as researchers from the University of Basel have shown in a study in Cell Reports. Their findings could be applied to the further development of cochlear implants.
-
 +11 +2
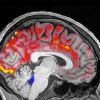
+11 +2A type of brainwave may help clean your brain while you sleep
As you sleep, slow waves of electrical activity in your brain seem to help rinse away harmful waste products that could otherwise damage your brain cells. The process may play a role in preventing neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease.
-
 +11 +3
+11 +3What it feels like to swim in sub-zero waters
Plunging into the ocean near Antarctica, Lewis Pugh was determined to push the limits of human endurance
-
 +4 +1
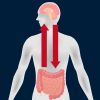
+4 +1The Vagus Nerve May Carry Serotonin Along the Gut-Brain Axis
When Prozac was introduced in 1987, it made a big splash as the first selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressant for the treatment of major depressive disorder. Prozac and Sarafem are brand names for a drug called "fluoxetine," which was first discovered by Eli Lilly in 1972. Since the patent for this drug expired in 2001, fluoxetine is available as a generic FDA-approved prescription for depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder, panic attacks, and some eating disorders.
-
 +19 +1
+19 +1Nomadic divers evolve larger spleens to stay underwater for 13 minutes, scientists find
A tribe of nomadic divers has evolved larger spleens to allow them to catch fish more than 200 feet underwater, scientists have discovered.
-
 +2 +1
+2 +1Repeated Periods of Poverty Accelerate the Ageing Process
Genetics, lifestyle and environment are all factors that somehow influence when and how we all age. But the financial situation is also important. Now, researchers from the Center for Healthy Aging and the Department of Public Health have found that four or more years with an income below the relative poverty threshold during adult life make a significant difference as to when the body begins to show signs of ageing.
-
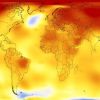 +23 +5
+23 +5Heatwave: think it's hot in Europe? The human body is already close to thermal limits elsewhere
Already heat-stressed countries will see the largest absolute increases in humid-heat and have the least ability to adapt.
-
 +40 +7
+40 +7One Type of Sitting May Pose a Greater Risk to Heart Health Than Others
As a society, we sit too much. We sit in the car, we sit at our desks, and we flop down on the couch when we get home. But not all sitting is made equal. Each of these approaches to sitting poses a very different risk to heart health, according to research published Wednesday in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
-
 +2 +1
+2 +1The human body is a mosaic of different genomes
Survey finds that ‘normal’ human tissues are riddled with mutations.
-
 +21 +5
+21 +5Almost all healthy people harbor patches of mutated cells
Even healthy tissues can build up mutations, some of which have been tied to cancer.
-
 +21 +4
+21 +4Sleep Apnea Can Have Deadly Consequences
The condition is on the rise because the most frequent cause is obesity, which continues its unrelenting climb among American adults.
-
 +18 +5
+18 +5Evolution of Walking Upright Linked to Ancient Supernova in Weird New Theory
A massive star explosion 2.6 million years ago may be the reason we walk on two feet.
-
 +32 +6
+32 +6Humans and Neanderthals Evolved from a Mystery Common Ancestor, Huge Analysis Suggests
Modern humans and Neanderthals may have diverged a long, long time ago, at least 800,000 years back.
Submit a link
Start a discussion




















