Neuroimaging study finds people who exercise more display an elevated brain response to reward
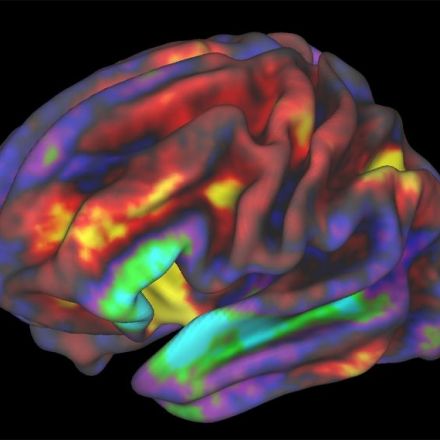
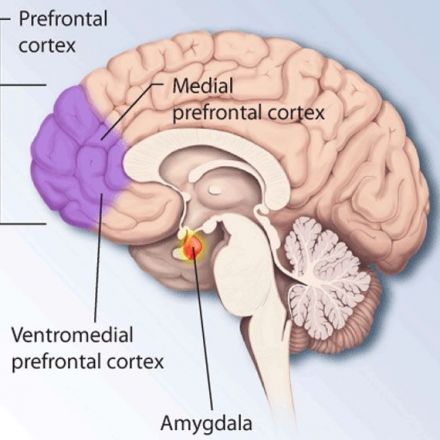
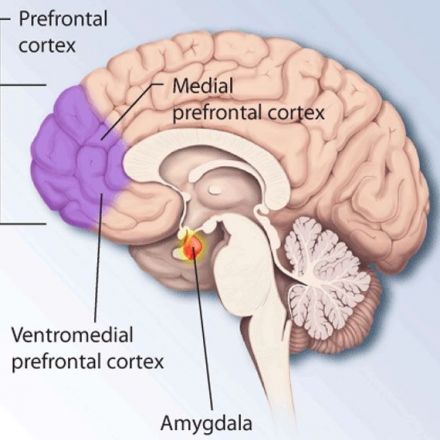
New research published in the journal Biological Psychology revealed that people who exercise more show increased brain activity when receiving an unexpected reward, specifically in the right medial orbitofrontal cortex. These findings may suggest that regular exercise alters the reward-circuit function, potentially reinforcing exercise behavior.
Continue Reading

























Join the Discussion