On Microbial Symbioses
Our new paper Better Together: Engineering and Application of Microbial Symbioses co-authored by Stephanie G Hays, William G Patric, Marika Ziesack, Neri Oxman and Pamela A Silver is out. Written in parallel to the creation of Mushtari, it considers wholes that are bigger than the sum of their parts by way of microbial symbiosis.
Continue Reading-
Better together: engineering and application of microbial symbioses
Symbioses provide a way to surpass the limitations of individual microbes. Natural communities exemplify this in symbioses like lichens and biofilms that are robust to perturbations, an essential feature in fluctuating environments. -
Mediated Matter
The Mediated Matter group focuses on Nature-inspired Design and Design-inspired Nature. We conduct research at the intersection of computational design, digital fabrication, materials science and synthetic biology -
Examples of natural metabolic cooperation
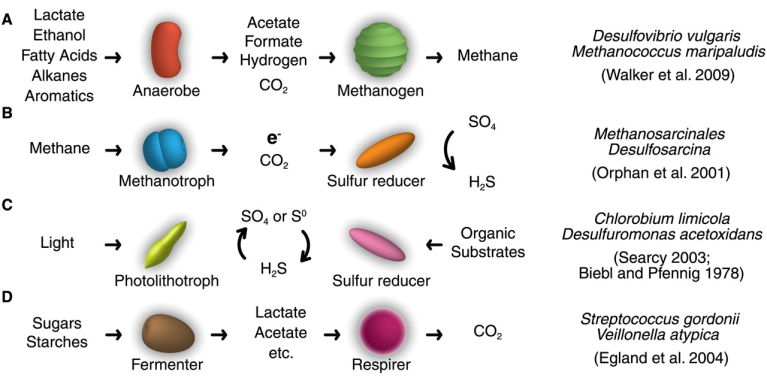 Most natural syntrophic relationships involve the exchange of waste or metabolic by-products. The right column notes an example pair of partners for each class of interaction.
Most natural syntrophic relationships involve the exchange of waste or metabolic by-products. The right column notes an example pair of partners for each class of interaction.
-
Dynamics in the mixed microbial concourse
Isolated, clonal populations of cells are rarely found in nature. The emergent properties of microbial consortia present a challenge for the systems approach to biology, as chances for competition, communication, or collaboration multiply with the number of interacting agents. -
Microbial Symbiosis
Microbial Symbiosis is devoted to communicating cutting-edge research on symbiotic microbial interactions where symbiosis is defined as any permanent or stable association between a microbe and at least one other organism. -
Cooperation and spatial distribution
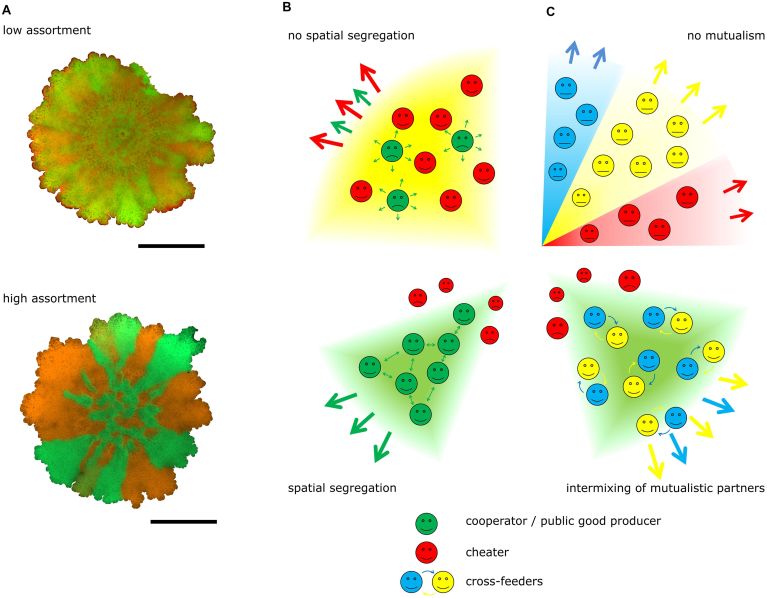 Experimental examples of Bacillus subtilis colony biofilms are shown with low (above) and high (below) spatial assortment of genetically identical strains with different fluorescent labels.
Experimental examples of Bacillus subtilis colony biofilms are shown with low (above) and high (below) spatial assortment of genetically identical strains with different fluorescent labels.
-
Conflict and Cooperation in Microbial Societies
The most evident aspect of biodiversity is the variety of complex forms and behaviors among organisms, both living and extinct. Comparative molecular and physiological studies show that the evolution of complex phenotypic traits involves multiple levels of biological organization.
Additional Contributions:


























Join the Discussion