Enhanced Longevity by Ibuprofen, Conserved in Multiple Species, Occurs in Yeast through Inhibition of Tryptophan Import
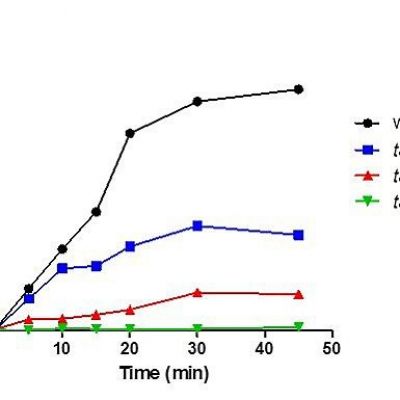
Author Summary Aging is the greatest risk factor for many diseases, which together account for the majority of global deaths and healthcare costs. Here we show that the common drug ibuprofen increases the lifespan of yeast, worms and flies, indicative of conserved longevity effects. In budding yeast, an excellent model of cellular longevity mechanisms, ibuprofen's pro-longevity action is independent of its known anti-inflammatory role. We show that the critical function of ibuprofen in longevity is to inhibit the uptake of aromatic amino acids, by destabilizing the high-affinity tryptophan permease. We further show that ibuprofen alters cell cycle progression. Mirroring the effects of ibuprofen, we found that most yeast long-lived mutants were also similarly affected in cell cycle progression. These findings identify a safe drug that extends the lifespan of divergent organisms and reveal fundamental cellular properties associated with longevity.
Continue Reading


























Join the Discussion