-
 +17 +1
+17 +1Potential New Treatment for “Brain Fog” in Long COVID Patients
Individuals with long COVID, sometimes referred to as “long-haulers,” experience symptoms that may persist for weeks, months, or even years after their acute viral infection. While symptoms vary widely, a common complaint among patients is “brain fog”—a colloquial term for significant, persistent cognitive deficits, with consistent impairment of executive functioning and working memory.
-
 +17 +1
+17 +1First human trials test light & sound therapy for Alzheimer's disease
A new study published in the journal PLoS ONE has reported on the first human tests of an experimental therapy using sound and light to treat Alzheimer's disease (AD). The initial findings are promising.
-
 +20 +1
+20 +1A low-dose of caffeine suppresses alpha brain waves and improves executive functioning
A study in Thailand using electroencephalography (EEG) and cognitive tests showed that working memory improved after drinking a caffeinated drink in the morning. Additionally, EEG recordings showed a reduction of alpha wave activity, a type of brain activity often associated with drowsiness, after drinking the caffeinated drink compared to the activity level before. The study was published in Physiology & Behavior.
-
 +23 +1
+23 +1Elon Musk Shows Off Monkey That Can Type With Brain Implant Instead of Typewriter
During a show and tell, Tesla and SpaceX CEO Elon Musk showed off what his brain computer interface (BCI) startup Neuralink has been working on.
-
 +15 +1
+15 +1A Promising Trial Targets a Genetic Risk for Alzheimer’s
Preliminary results offer hope that gene therapy can protect people with a version of the brain disease driven by a particular gene variant.
-
 +3 +1
+3 +1What it’s like to live with brain fog
Brain fog, which includes impaired attention, concentration, memory and processing speed, can be debilitating.
-
 +16 +1
+16 +1Puzzling changes were discovered in the brains of people who suffer from migraines
A new bit of research has discovered several puzzling changes in the brains of individuals that suffer from migraines
-
 +23 +1
+23 +1Brain-Powered Wheelchair Shows Real-World Promise
In one of the first studies of its kind, several people with motor disabilities were able to operate a wheelchair
-
 +19 +1
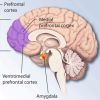
+19 +1Neuroimaging study suggests smartphone addiction may reduce the capacity for creativity
Researchers in China investigated the consequences of smartphone addiction on creativity. Using brain imaging technology, they measured cortical responses to creative tasks. The results indicate that smartphone addiction negatively influences the brain’s creative capacity. Specifically, the brain’s prefrontal cortex and temporal areas were not as active when asked to think creatively. This was in contrast to participants who did not have a smartphone addiction.
-
 +15 +1
+15 +1Popular ‘anti-aging’ supplement may lead to brain cancer, study says
A popular anti-aging vitamin may lead to an increased risk of brain cancer, according to a new MU study.
-
 +16 +1
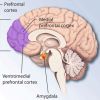
+16 +1New study links suffering from long-lasting severe depression to reduction in brain volume
A study on a large sample of patients found chronic, long-lasting depression to be associated with reduced brain volume. The reduced volume was found in brain regions relevant for planning one’s behavior, focusing attention, thinking, learning and remembering and also in regions relevant for regulating emotions. The study was published in Neurobiology and Treatment of Depression.
-
 +19 +1
+19 +1New research suggests that those with bipolar I and a history of migraines should avoid taking lithium
A new study in Brain and Behavior has unraveled the relationship between migraines, bipolar disorder, and patient outcomes. Nicole Sekula and colleagues conducted an 11-year longitudinal study demonstrating that those with bipolar disorder and migraines experienced worse symptoms of depression, mania, and a diminished quality of life on average. In addition, if those individuals were also prescribed lithium, their symptoms of mania were worse than those with migraines not taking lithium.
-
 +17 +1
+17 +1Mind-reading AI works out what you are thinking from brain scans
A brain decoder can extract words and sentences from the brain recordings of people listening to stories or watching silent films
-
 +14 +1
+14 +1Exposure to environmental toxins may be root of rise in neurological disorders
Doctors warn exposure to omnipresent yet poorly understood chemicals such as microplastics could play a role in dementia
-
 +19 +1
+19 +1Why Some People Conjure Terrifying ‘Sleep Paralysis Demons,’ According to a Neuroscientist
Neuroscientist Ben Rein explains the strange phenomenon of hallucinating while on the edge of consciousness.
-
 +9 +1
+9 +1New window into brain’s computational function
The function of the human brain is exceptional, driving all aspects of our thoughts and creativity. Yet the part of the human brain – the neocortex – responsible for such cognitive functions has a similar overall structure to other mammals.
-
 +17 +1
+17 +1This Is Your Brain On Drug Ads
Apologies to listeners who received two episodes in their feed today. The U.S. is one of two countries in the world that allows pharmaceutical companies to advertise prescription drugs directly to consumers. Why? And what does that do to us Subscribe to our weekly newsletter here.
-
 +16 +1
+16 +1Human brain cells transplanted onto rat brain can influence its behavior, Stanford study suggests
Researchers were able to confirm that sensations from the rat's whiskers were being processed by the human brain cells. They also engineered cells that were sensitive to a colored light, then taught the rat to associate the light with a reward.
-
 +17 +1
+17 +1Stress eating? Here’s how to train your brain to crave healthy foods.
Stress and anxiety can promote belly fat and cravings, making you eat more. But you can train your brain to crave healthier foods during stressful times.
-
 +22 +1
+22 +1Neuroscientists unravel the mystery of why you can’t tickle yourself
New study shows how tickling, playfulness can address key questions about the brain.
Submit a link
Start a discussion




















