-
 +15 +1
+15 +1Visualizing the inside of cells at previously impossible resolutions provides vivid insights into how they work
Many microscopy techniques have won Nobel Prizes over the years. Advancements like cryo-ET that allow scientists to see the individual atoms of cells can reveal their biological functions.
-
 +11 +1
+11 +1Drug Turns Cancer Gene Into ‘Eat Me’ Flag for Immune System
Tumor cells are notoriously good at evading the human immune system; they put up physical walls, wear disguises and handcuff the immune system with molecular tricks. Now, UC San Francisco researchers have developed a drug that overcomes some of these barriers, marking cancer cells for destruction by the immune system.
-
 +15 +1
+15 +1Aging Is a Communication Breakdown
Genes that can’t express themselves may be hallmarks of cancer. By Jim Kozubek.
-
 +7 +1
+7 +1Cells Talk and Help One Another via Tiny Tube Networks
Long-overlooked “tunneling nanotubes” and other bridges between cells act as conduits for sharing RNA, proteins or even whole organelles. By Viviane Callier.
-
 +6 +1
+6 +1Neutrinos Suggest Solution to Mystery of Universe’s Existence
Updated results from a Japanese neutrino experiment continue to reveal an inconsistency in the way that matter and antimatter behave. From above, you might mistake the hole in the ground for a gigantic elevator shaft. Instead, it leads to an experiment that might reveal why matter didn’t disappear in a puff of radiation shortly after the Big Bang.
-
 +24 +1
+24 +1It's possible for one person to have two different sets of DNA — here's how it happens
Human chimeras are people with multiple sets of DNA. It sounds like science fiction, but it can happen totally naturally.
-
 +7 +1
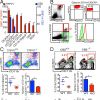
+7 +1Endocannabinoid system acts as a regulator of immune homeostasis in the gut
Exogenous cannabinoids such as marijuana exert their influence through cannabinoid receptors. Endogenous cannabinoids such as anandamide (AEA) function through the same receptors and their physiological roles are a subject of intense study. Here, we show that AEA plays a pivotal role in maintaining immunological health in the gut. The immune system in the gut actively tolerates the foreign antigens present in the gut through mechanisms that are only partially understood. We show that AEA contributes to this critical process by promoting the presence of CX3CR1hi macrophages, which are immunosuppressive.
-
 +2 +1
+2 +1Chip Reprograms Cells to Regenerate Damaged Tissue
A device delivers infusions of DNA and other molecules restored injured limbs in mice. By Simon Makin.
-
 +12 +1
+12 +1Like alchemists with killer precision, brown snakes make different venoms across their lifetime
There has been at least one fatal bite from a very small brown snake in Australia. But now we know that venom is different in adult and baby brown snakes. By Timothy N. W. Jackson.
-
 +1 +1
+1 +1Introducing ‘dark DNA’ – the phenomenon that could change how we think about evolution
Some animals seem to have missing genes – but the reality is a lot more intriguing. By Adam Hargreaves.
-
 +32 +1
+32 +1Scientists May Have Reactivated The Gene That Causes Neurons To Stop Growing
It’s commonly believed that brain cells stop multiplying when our bodies become fully grown. Researchers from the German Centre for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE) theorized that our bodies have a sort of “molecular break”, that signals the neurons to stop growing when adulthood is reached. Reawakening neurons past this “break” could be key to treating diseases that cause damage to the neural network.
-
 +29 +1
+29 +1Scientists Have Twisted Molecules Into The Tightest Knot Ever
This new knot has eight crossings, far more than previous molecular knots.
-
 +33 +1
+33 +1Did the Seeds of Life Come from Space?
Meteorites might have delivered some of the basic building blocks, but there are still some missing pieces to the puzzle. By Elizabeth Tasker.
-
 +19 +1
+19 +1Scientists are unlocking the mystery of how marijuana makes us get high
This will help us better understand how to use the drug for medical purposes. By Angela Chen.
-
 +24 +1
+24 +1How to Kill Antibiotic-Resistant ‘Superbugs’ Without Antibiotics
Because “superbugs” like MRSA no longer respond to traditional antibiotic treatments, researchers are locked in a constant microscopic arms race to develop new antibiotics that effectively counter increasingly resistant opportunistic bacterial strains. Recently, a 25-year-old doctoral student developed an entirely new technique for combating superbugs- and without using antibiotics... By Zayan Guedim.
-
 +7 +1
+7 +1Tasmanian devil milk fights superbugs
Milk from Tasmanian devils could offer up a useful weapon against antibiotic-resistant superbugs, according to Australian researchers.
-
 +13 +1
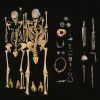
+13 +1Reconstructing the sixth century plague from a victim
Before the infamous Black Death, the first great plague epidemic was the Justinian plague, which, over the course of two centuries, wiped out up to an estimated 50 million (15 percent) of the world's population throughout the Byzantine Empire—and may have helped speed the decline of the eastern Roman Empire.
-
 +2 +1
+2 +1Viruses Find Love In A Boiling Place
Odd viruses flourish in boiling, acidic Yellowstone hot springs. By Joel Shurkin.
-
 +27 +1
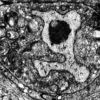
+27 +1A newly discovered way for cells to die
Some cells are meant to live, and some are meant to die. The linker cell of Caenorhabditis elegans, a tiny worm that is a favored model organism for biologists, is among those destined for termination…
-
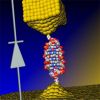 +19 +1
+19 +1World’s Smallest Diode Is Made of DNA
New device could help advance the field of molecular electronics
Submit a link
Start a discussion




















