-
 +15 +4
+15 +4Like Monstrosities from Another World
The gas mask's grip on our collective consciousness.
-
 +23 +4
+23 +4Odours have a complex topography, and it’s been mapped by AI
We can split light by a prism, sounds by tones, but surely the world of odour is too complex and personal? Strangely, no
-
 +30 +5
+30 +5Well, I never: AI is very proficient at designing nerve agents
Researchers for a pharmaceutical company stumbled upon a nightmarish realisation, proving there’s nothing intrinsically good about machine learning
-
 +17 +4
+17 +4Magnetic solution removes toxic "forever chemicals" from water in seconds
Scientists in Australia have developed an intriguing new technique for removing toxic “forever chemicals” from water. Adding a solution to contaminated water coats the pollutants and makes them magnetic, so they can easily be attracted and isolated.
-
 +29 +4
+29 +4PFAS left dangerous blood compounds in nearly all US study participants
Nearly all participants in a new study looking at exposure to PFAS “forever chemicals” in the US state of North Carolina have multiple dangerous compounds in their blood, and most at levels that researchers say requires medical screening. The North Carolina State University study, which is among the largest ever conducted, checked about 1,500 blood samples from people living in the Cape Fear River basin over several years. It’s the first study to recommend screening for cancers, kidney damage, heart disease and other health issues linked to the chemicals, using newly developed physicians’ guidelines for PFAS exposure.
-
 +16 +2
+16 +2The Toxic History of Color
For all of human history, our species have used both natural and synthetic dyes—but have we taken our obsession with color to an extreme?
-
 +21 +5
+21 +5Best Selling Organic Chemistry Textbook Goes Open Access After Professor Regains The Copyright
It’s well known that textbook prices are generally high. That’s in part because academic publishers effectively have a monopoly when it comes to standard texts. Very often, these are texts that stu…
-
 +11 +1
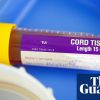
+11 +1‘Forever chemicals’ detected in all umbilical cord blood in 40 studies
Studies collectively examined nearly 30,000 samples over the past five years in ‘disturbing’ findings
-
 +3 +1
+3 +1School uniforms in N America linked to PFAS "forever chemicals"
A study of school uniforms in the US and Canada shows high levels of chemical substances linked to health issues.
-
 +20 +1
+20 +1Researchers develop a reactor that can destroy 'forever chemicals'
"Forever chemicals," named for their ability to persist in water and soil, are a class of molecules that are ever-present in our daily lives, including food packaging and household cleaning products. Because these chemicals don't break down, they end up in our water and food, and they can lead to health effects, such as cancer or decreased fertility.
-
 +21 +4
+21 +4New plant-derived composite is tough as bone and hard as aluminum
The strongest part of a tree lies not in its trunk or its sprawling roots, but in the walls of its microscopic cells. A single wood cell wall is constructed from fibers of cellulose—nature's most abundant polymer, and the main structural component of all plants and algae. Within each fiber are reinforcing cellulose nanocrystals, or CNCs, which are chains of organic polymers arranged in nearly perfect crystal patterns. At the nanoscale, CNCs are stronger and stiffer than Kevlar. If the crystals could be worked into materials in significant fractions, CNCs could be a route to stronger, more sustainable, naturally derived plastics.
-
 +13 +2
+13 +2Formula for Beauty: The Geo-Chemistry Behind Rookwood Pottery
Being an amateur geologist is probably not a bad avocation for a glaze chemist.
-
 +19 +9
+19 +9The name’s bond, chemical bond
Kathryn Harkup explores the poisons - real and fictional - used in Bond films
-
 +16 +4
+16 +4How chlorine stabilizes next-gen solar cells at an atomic scale
A team of researchers led by Professor Yabing Qi in the Energy Materials and Surface Sciences Unit at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST) in Japan have imaged the atoms at the surface of the light-absorbing layer in a new type of next-generation solar cells, made from a crystal material called metal-halide perovskite.
-
 +15 +3
+15 +3Using electricity to give chemistry a boost
Metal organic frameworks (MOFs) are a promising class of materials that have many applications as catalysts, sensors and for gas storage. Widely studied over the past two decades, MOFs are typically produced using chemical processes that require high heat and high pressure.
-
 +22 +1
+22 +1Toxic ‘forever chemicals’ contaminate indoor air at worrying levels, study finds
Food and water were thought to be the main ways humans are exposed to PFAS, but study points to risk of breathing them in
-
 +14 +4
+14 +4In A World First, Scientists Made Human Milk Outside of the Breast
Breastfeeding can be complicated for many women. However, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends that infants be exclusively breastfed for about the first 6 months with continued breastfeeding. This is easier said than done as latching issues, fussy babies, discomfort and pain, and inadequate milk supply can often complicate matters.
-
 +30 +4
+30 +4A Key Property of Life Has Been Detected From High Altitude For The First Time
Hold up your hands in front of your face. For most people, they will be mirrored copies of each other: You can hold them palm-to-palm and they will match up, but you cannot superimpose them.
-
 +15 +3
+15 +3Extraordinary new material shows zero heat expansion from 4 to 1,400 K
Australian researchers have created what may be one of the most thermally stable materials ever discovered. This new zero thermal expansion (ZTE) material made of scandium, aluminum, tungsten and oxygen did not change in volume at temperatures ranging from 4 to 1400 Kelvin (-269 to 1126 °C, -452 to 2059 °F).
-
 +14 +3
+14 +3Alcohol, health, and the ruthless logic of the Asian flush
Say you’re an evil scientist. One day at work you discover a protein that crosses the blood-brain barrier and causes crippling migraine headaches if someone’s attention drifts while driving. Despite being evil, you’re a loving parent with a kid learning to drive. Like everyone else, your kid is completely addicted to their phone, and keep refreshing their feeds while driving. Your suggestions that the latest clown squirrel memes be enjoyed later at home are repeatedly rejected.
Submit a link
Start a discussion




















