-
 +21 +1
+21 +1Chlamydia cousin discovered in deep Arctic Ocean
The newfound bacteria might shed light on how chlamydia came to infect host organisms, like us.
-
 +21 +1
+21 +1Arctic permafrost thaw plays greater role in climate change than previously estimated
Abrupt thawing of permafrost will double previous estimates of potential carbon emissions from permafrost thaw in the Arctic, and is already rapidly changing the landscape and ecology of the circumpolar north, a new CU Boulder-led study finds.
-
 +4 +1
+4 +1Unique Sled Dogs Helped the Inuit Thrive in the North American Arctic
Inuit sled dogs have changed little since people migrated with them to the North American Arctic across the Bering Strait from Siberia, according to researchers who have examined DNA from the dogs from that time span. The legacy of these Inuit dogs survives today in Arctic sled dogs, making them one of the last remaining descendant populations of indigenous, pre-European dog lineages in the Americas.
-
 +21 +1
+21 +1Alaska is having a hell of a time growing sea ice
"We've got these incredibly warm seas."
-
 +16 +1
+16 +1As the Arctic heats up, what’s in store for its food webs?
The view from Kongsfjorden, Svalbard, is endless snow-covered mountains and glassy, frigid water. You need to travel roughly 400 miles west from the remote Norwegian archipelago to reach the northeast coast of Greenland.
-
 +11 +1
+11 +1Poppies, dandelions and daisies bloom in never before seen Arctic oases
‘Blooming’ might be the last word to associate with the Arctic, yet pictures below show meadows bursting with life as brightly-coloured flowers blossom in lush green grass. And while vegetation in khasyreis, basins of drained Arctic lakes, is less of a surprise, researchers discovered ‘bursts of life’ next to a residential settlement where permafrost ice veins were broken when people dug sand pits.
-
 +17 +1
+17 +1Largest ever polar expedition will soon be frozen in drifting sea ice
The biggest scientific project ever to take place in the Arctic is about to kick off. Within days, a ship is set to begin drifting in the sea ice off Siberia, from where it will eventually become locked in the ice for months of the Arctic winter. The Polarstern icebreaker is set to depart from Norway on 20 September – around the same time that researchers are expected to confirm the area of Arctic sea ice has reached the second lowest level on record. The ship is part of an epic endeavour called MOSAIC, which will involve some 600 scientists studying climate change, Arctic wildlife and more over the course of a year.
-
 +4 +1
+4 +1Radical proposals to 'refreeze' the Arctic
Iceberg-making submarines and "cloud brightening" are among the geoengineering solutions that could help replenish polar sea ice.
-
 +31 +1
+31 +1200 reindeer died on an Arctic Island -- and researchers think climate change is to blame
More than 200 reindeer have been found dead this summer in the Norwegian archipelago of Svalbard -- and climate change appears to be the killer, researchers say.
-
 +11 +1
+11 +1The Arctic is on fire
More than 100 intense 'unprecedented' wildfires have ravaged the Arctic since June
-
 +24 +1
+24 +1Unprecedented fires burn the Arctic
Smoke is rising over the forests of Alaska and Siberia. The World Meteorological Organization called the wildfires now burning around the Arctic "unprecedented." The United Nations agency noted that over 100 intense fires burned in the Arctic Circle alone over the past six weeks, releasing more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere than Sweden does in an entire year.
-
 +5 +1
+5 +1Scientists 'speechless' at Arctic fox's epic trek
A young fox has walked from Norway's Arctic islands to Canada in just 76 days.
-
 +11 +1
+11 +1The poisons released by melting Arctic ice
Toxic chemicals, anthrax - even nuclear waste - could be unleashed by global warming
-
 +17 +1
+17 +1The Poisons Released by Melting Arctic Ice
Toxic chemicals, anthrax - even nuclear waste - could be unleashed by global warming
-
 +3 +1
+3 +1Climate crisis: Alaska is melting and it’s likely to accelerate global heating
The state has just had its warmest spring on record, causing permafrost to thaw and dramatically reshaping some areas
-
 +13 +1
+13 +1Canadian Arctic fossils are oldest known fungus on Earth
Tiny fossils found in mudrock in the barren wilderness of the Canadian Arctic are the remains of the oldest known fungus on Earth, scientists say. The minuscule organisms were discovered in shallow water shale, a kind of fine-grained sedimentary rock, in a region south of Victoria island on the edge of the Arctic Ocean. Tests on the shale, which accumulated over millions of years in a river or lake, revealed that it formed between 900m and 1bn years ago in what is now the Northwest Territories.
-
 +33 +1
+33 +1Permafrost is thawing in the Arctic so fast that scientists are losing their equipment
Permafrost in some areas of the Canadian Arctic is thawing so fast that it's gulping up the equipment left there to study it.
-
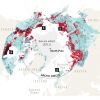 +7 +1
+7 +1Permafrost collapse is accelerating carbon release
The sudden collapse of thawing soils in the Arctic might double the warming from greenhouse gases released from tundra, warn Merritt R. Turetsky and colleagues.
-
 +7 +1
+7 +1Melting permafrost in Arctic will have $70tn climate impact – study
The release of methane and carbon dioxide from thawing permafrost will accelerate global warming and add up to $70tn (£54tn) to the world’s climate bill, according to the most advanced study yet of the economic consequences of a melting Arctic. If countries fail to improve on their Paris agreement commitments, this feedback mechanism, combined with a loss of heat-deflecting white ice, will cause a near 5% amplification of global warming and its associated costs, says the paper, which was published on Tuesday in Nature Communications.
-
 +3 +1
+3 +1Air temperatures in the Arctic are driving system change
A new paper shows that air temperature is the “smoking gun” behind climate change in the Arctic, according to John Walsh, chief scientist for the UAF International Arctic Research Center. Several University of Alaska Fairbanks researchers are co-authors on the paper, which says that “increasing air temperatures and precipitation are drivers of major changes in various components of the Arctic system.”
Submit a link
Start a discussion




















