-
 +21 +1
+21 +1Sugar disrupts microbiome, leading to metabolic disease and diabetes
A new study found that sugar consumption disrupts the microbiome and leads to a loss of immune cells in mice. The researchers draw a strong connection between the loss of these immune cells and cardiometabolic diseases, such as diabetes.
-
 +14 +1
+14 +1Prehistoric teeth hint at Stone Age sex with Neanderthals
A new analysis of 11 teeth found in a cave in Jersey, an island in the English Channel, suggests that some of them could have belonged to individuals that had mixed Neanderthal and early modern human ancestry.
-
 +18 +1
+18 +1Positive Outlook Predicts Less Memory Decline
The happier we feel, the less likely we are to experience memory decline.
-
 +15 +1
+15 +1Tunguska explosion in 1908 caused by asteroid grazing Earth
A new theory explains the mysterious explosion in Siberia, scientists say, suggesting Earth barely escaped a far greater catastrophe.
-
 +9 +1
+9 +1Researchers Find The Upper Limit For The Speed Of Sound
An international research collaboration has discovered the fastest possible speed of sound. The upper limit was found to be about 36 km per second.
-
 +13 +1
+13 +1Germany's largest meteorite discovered after sitting for decades in garden
The out-of-this-world find is being hailed as a "scientific sensation." The meteorite was first dug up in 1989 and sat in a garden for decades before the homeowner shared his unusual rock with researchers.
-
 +20 +1
+20 +1Soil gets its smell from bacteria trying to attract invertebrates
Soil’s earthy smell comes from chemicals produced by bacteria called Streptomyces, which use the odour to attract springtails to help disperse their spores
-
 +13 +1
+13 +1'Ghost' population of humans discovered in ancient Africa
This is the first time researchers have done an in-depth analysis of ancient DNA from western Central Africa.
-
 +13 +1
+13 +1What happens if you have no word for 'dinosaur'
English is the world’s dominant scientific language, yet it has no word for the distinctive smell of cockroaches. What happens though, if you have no words for basic scientific terms?
-
 +2 +1
+2 +17 Billion-Year-Old Stardust Is Oldest Material Found on Earth
Some of these ancient grains are billions of years older than our sun.
-
 +19 +1
+19 +1Neanderthals 'dived in the ocean' for shellfish
Until now, there's been little evidence our evolutionary relatives could swim.
-
 +3 +1
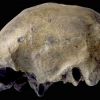
+3 +1Homo erectus’ last known appearance dates to roughly 117,000 years ago
New evidence helps resolve a debate over how long ago Home erectus survived in what’s now Indonesia, a study finds.
-
 +18 +1
+18 +1Why are big storms bringing so much more rain? Warming, yes, but also winds
For three hurricane seasons in a row, storms with record-breaking rainfall have caused catastrophic flooding in the southern United States. A new analysis by Princeton researchers explains why this trend is likely to continue with global warming: Both the higher moisture content of warmer air and storms’ increasing wind speeds conspire to produce wetter storms.
-
 +17 +1
+17 +1Frédéric Leroy: meat's become a scapegoat for vegans, politicians & the media because of bad science
-
 +3 +1
+3 +1Human bodies can move on their own after death, study finds
Dead bodies move on their own after death — likely due to processes of decomposition, researchers suspect, pointing to implications for forensic science.
-
 +17 +1
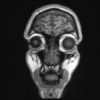
+17 +1A Boy Ate Only Chips And French Fries For 10 Years. This Is What Happened To His Eyes.
This case is based on publication in literature by Harrison R, Warburton V, Lux A, Atan D. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Sep 3.
-
 +3 +1
+3 +1Team behind world's first black hole image wins 'Oscar of science'
The 347 scientists who collaborated to produce the world's first image of a black hole were honored Thursday with the Breakthrough Prize in Fundamental Physics, winning $3 million dollars for what is known as the "Oscars of science."
-
 +21 +1
+21 +1Doctors altered a person's genes with CRISPR for the first time in the U.S. Here's what could be next.
Last week, a young woman with sickle cell anemia became the first person in the United States to have her cells altered with CRISPR gene editing technology. Here's what that means for the future treatment of genetic diseases.
-
 +9 +1
+9 +1Teens ‘Mocked’ by Parents at Greater Risk for Bullying, Victimization
A unique longitudinal study provides a more complete understanding of how parents’ belittling and critical interactions with adolescents thwart their ability to maintain positive relationships with peers.
-
 +4 +1
+4 +1How Do We Solve the Problem of Predators?
Wolves pose a uniquely difficult conservation issue.
Submit a link
Start a discussion





















